Want to stop brute force attacks on WordPress sites? Read our step-by-step guidelines to prevent your WordPress site from brute force attacks and make it more secure.
You would be surprised to know that about thirty thousand websites are hacked every day. And, every 39 seconds, a new cyberattack happens on the web. The brute force attack is one of the common and regular attacks on any type of website. But, when your website is in WordPress you have some ways to stop brute force attacks.
In simple language, brute force attacks are like a burglar trying every key in the neighborhood until they find the one that opens the door. In the case of WordPress websites, they can keep trying different usernames and passwords until they get it right because there’s no limit to their attempts.
In our article, we will discuss brute force attacks in detail, analyze the impacts, and describe ways to prevent WordPress sites from brute force attacks in some easy ways.
What Are Brute Force Attacks?
A brute force attack is a hacking method where attackers try all possible combinations of usernames and passwords until they find the right one to gain unauthorized access to a system, website, or account.

It’s like a burglar trying every key in existence until they find the one that fits the lock, allowing them to break in and access sensitive information or control the system. This method relies on the attacker’s patience and computing power to crack the security credentials.
Why Stop Brute Force Attacks on WordPress Sites?
Brute force attacks can have serious consequences on your websites and business. Suppose the attacker gets access to your website in some way. In that case, they can do anything that can harm your reputation, steal your and your user’s data, take away website ownership from you, and ruin your business if your website and business aren’t protected that way.
Brute force attacks can have the following consequences on your website and business.
Lose Website Access to Unauthorized Individuals
Successful brute force attacks give attackers unauthorized access to the WordPress site. Once inside, they can manipulate, steal, or delete data, deface the site, or even take control of the entire website.
Lose Your and Your Users’ Data
Attackers can steal sensitive user data, including email addresses, passwords, and personal information. This data can be misused for identity theft or other malicious activities.
Malware Injection
Once hackers get access to your website, they might inject malicious code into the website, which can infect visitors’ computers or compromise their security, leading to further attacks or data breaches.
Server Overload
Brute force attacks involve multiple login attempts, overwhelming the server with traffic. This can slow down the site, making it inaccessible to legitimate users and causing a negative user experience.
Financial Loss
For businesses relying on their WordPress sites for e-commerce, a successful brute force attack can lead to financial losses due to downtime, decreased sales, or the cost of repairing and securing the website.
To mitigate these risks, WordPress site owners must implement strong security measures, such as limiting login attempts, using complex passwords, enabling two-factor authentication, and regularly updating plugins and themes to ensure their sites are protected against brute force attacks.
How to Stop Brute Force Attacks on WordPress Sites?
There are many different ways to stop brute force attacks on WordPress sites. As brute force attacks are all about guessing login credentials and getting access to a website, you need to strengthen your login system to prevent such attacks.
We are using a WordPress security plugin to do that. The plugin we will be using for this tutorial is SolidWP formerly known as iTheme security. It is a WordPress security plugin that can help you with brute force attack protection, scan for vulnerable plugins and themes, Increase user login security with 2FA, and many more.
So, let’s get started:
Step 1: Install SolidWp WordPress Security Plugin
First of all, you need to install the SolidWP WordPress security plugin formerly known as the iTheme security WordPress plugin. Install the plugin as you do any regular plugin in WordPress.
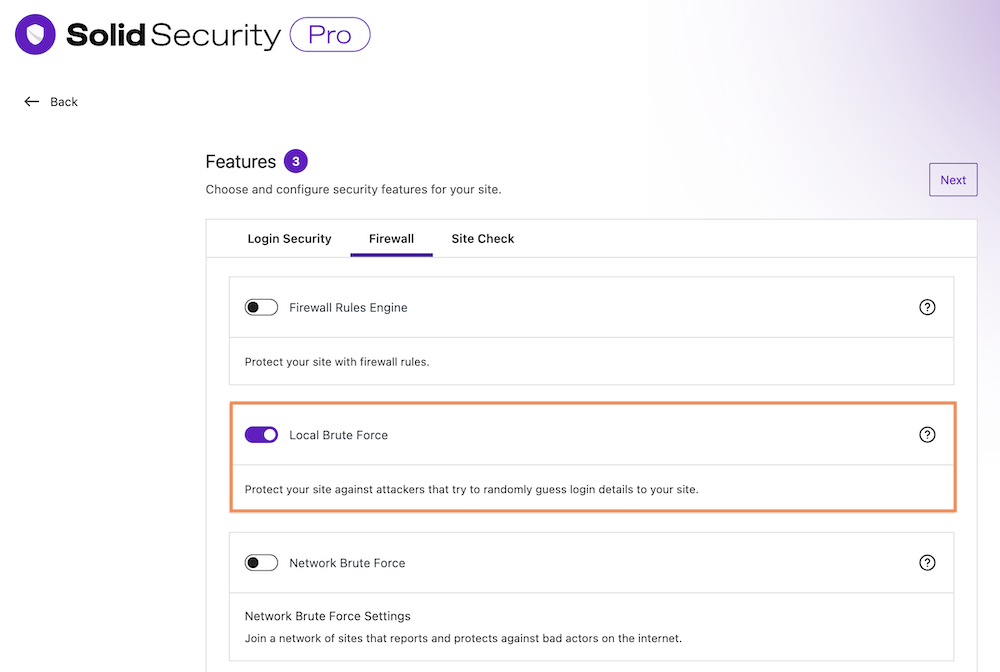
Step 2: Enable Local Brute Force Protection
Once you have installed the plugin, go to your WordPress dashboard > Security > Settings. Click on Features > Firewall, scroll down to the “Local Brute Force” section, and enable it.
Step 3: Limit Maximum Login Attempts Per Host On WordPress Site
The brute force attack is all about attempting to log in to your site with multiple possible login credentials. Week passwords and usernames make your website vulnerable to brute force attacks. You can limit the number of login attempts per host on your WordPress site.
Go to your WordPress dashboard > Security > Settings. Click on Features > Firewall, and scroll down to the “Local Brute Force” section. Now define how many login attempts you want to allow before an IP is locked out of the system by giving the number in the “MAX LOGIN ATTEMPTS PER IP” box.
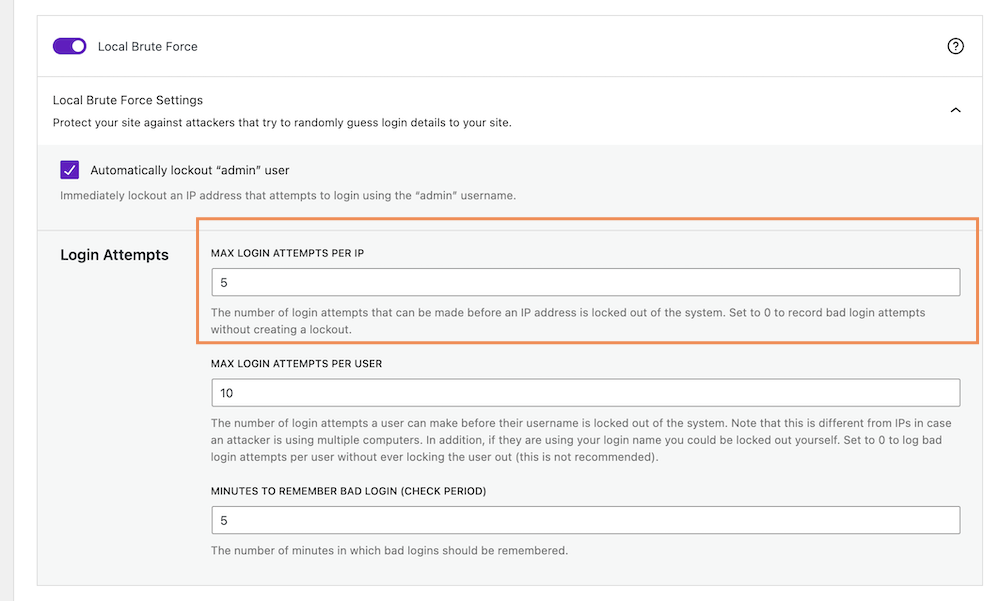
Note: The number of login attempts a user has before their host or computer is locked out of the system. Set to 0 to record bad login attempts without locking out the host.
Step 4: Limit Max Login Attempts Per User on WordPress Sites
In case attackers know your login usernames, they could be using different computers to log in to your website. With the Solid WP Security plugin, you can limit the login attempts per user on your WordPress site too.
Go to your WordPress dashboard > Security > Settings. Click on Features > Firewall, and scroll down to the “Local Brute Force” section. Now define how many login attempts by a user you want to allow before an IP is locked out of the system by giving the number in the “MAX LOGIN ATTEMPTS PER USER” box.
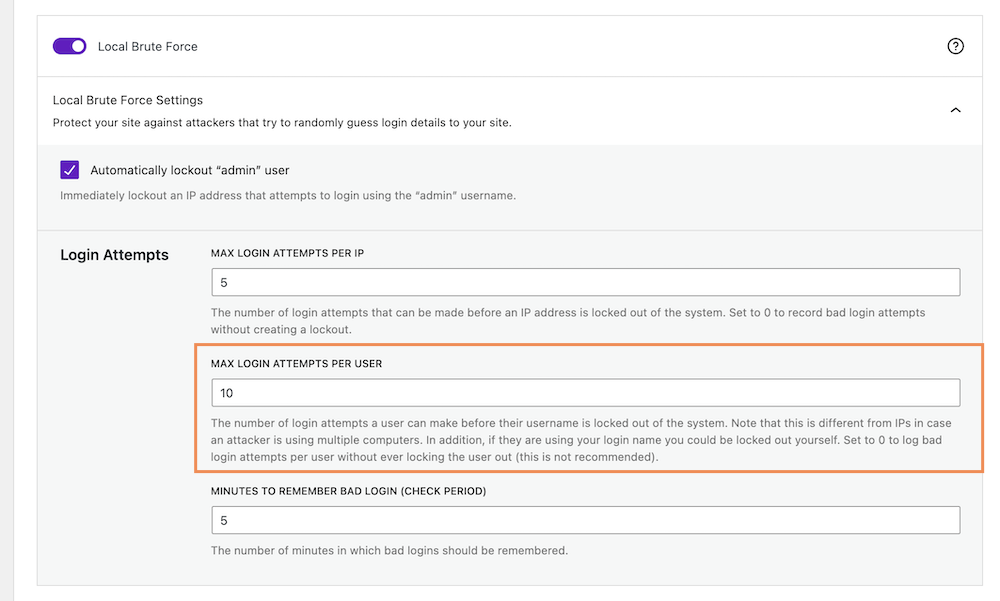
Note: The number of login attempts a user has before their username is locked out of the system. Note that this is different from hosts in case an attacker is using multiple computers. In addition, if they are using your login name you could be locked out yourself. Set to zero to log bad login attempts per user without ever locking the user out (this is not recommended)
Step 5: Stop Bad Login From Getting Access
You can lock the hosts attempting to log in to your website using the wrong username and password. You can set how long your website will lock the user.
Go to your WordPress dashboard > Security > Settings. Click on Features > Firewall, and scroll down to the “Local Brute Force” section. Now define the number of minutes in which a bad login will be remembered. “MINUTES TO REMEMBER BAD LOGIN (CHECK PERIOD)” box.
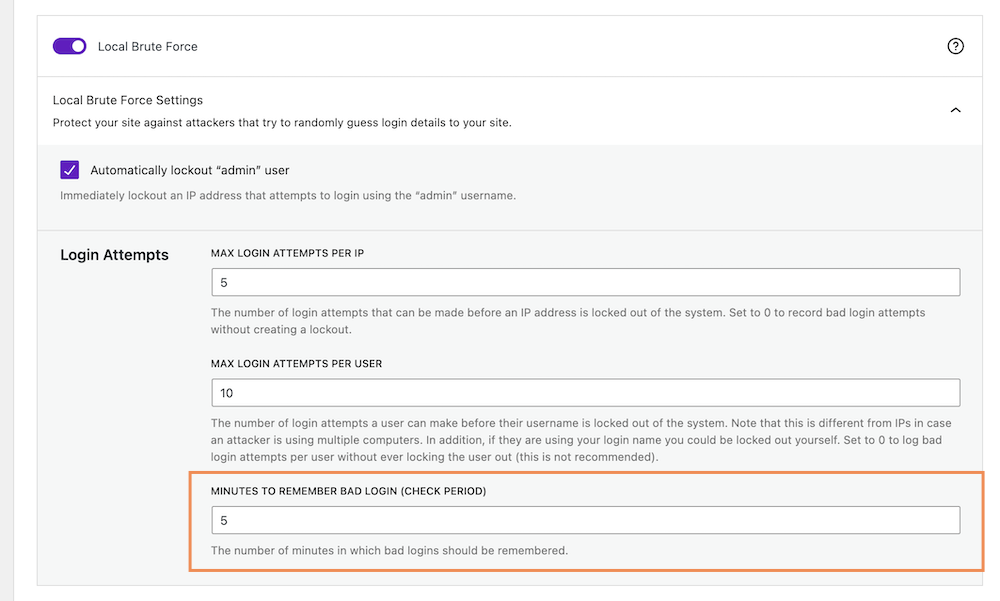
Step 6: Ban Host Attempting to Login With “Admin” Username
Admin is the common username in websites. So, attackers try to log in to the website with an “Admin” username first. It is better to avoid any such common username. You can also ban the host who is trying to log in with this username.
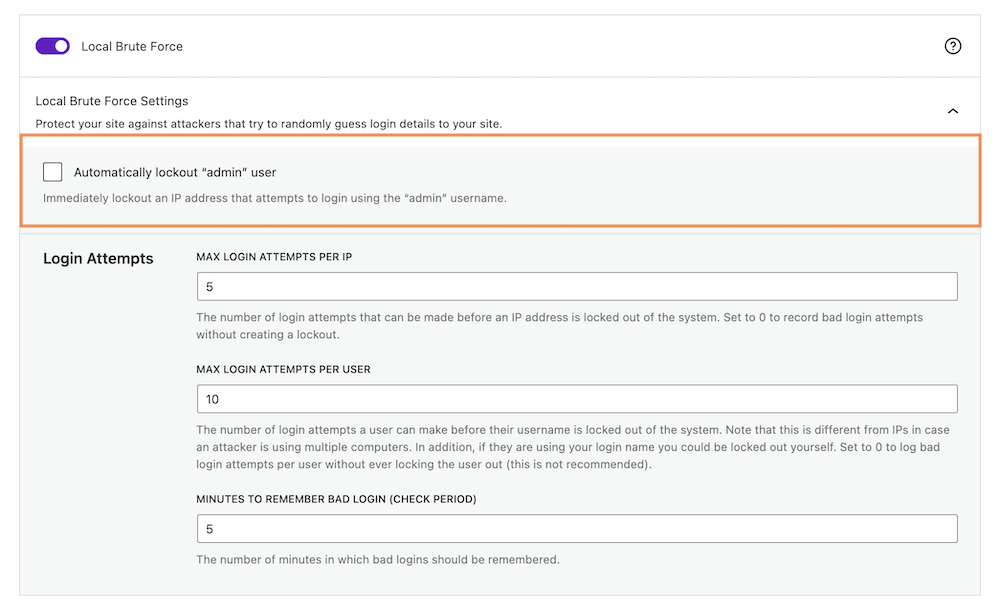
Go to your WordPress dashboard > Security > Settings. Click on Features > Firewall, and scroll down to the “Local Brute Force” section. Checkmark on “Automatically lockout “admin” user” to lock out an IP address that attempts to log in using the “admin” username immediately.
It will identify the host trying to log in with an “admin” username and Immediately ban a host that attempts to log in.
Step 7: Ban IPs Hitting Your Website
Local brute force protection looks only at attempts to access your site and bans users per the lockout rules specified locally. Network brute force protection takes this a step further by banning users who have tried to break into other sites from breaking into yours. The network protection will automatically report the IP addresses of failed login attempts to SolidWP and will block them for the length of time necessary to protect your site based on the number of other sites that have seen a similar attack.
Go to your WordPress dashboard > Security > Settings. Click on Features > Firewall, and scroll down to the “Network Brute Force” section. Place your email address to set up API configuration.
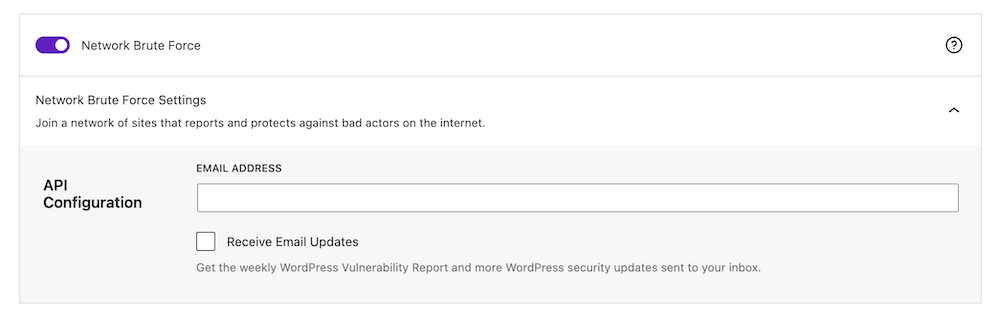
You can join a network of sites that report and protect against bad actors on the internet. The API key will be added automatically upon placing the email address.
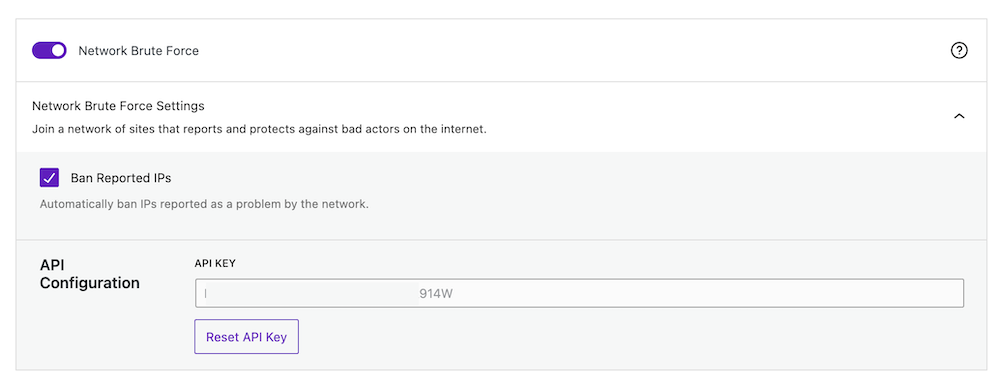
Save the changes to make the updates work.
Apart from these ways to stop brute force attacks on WordPress sites, you can utilize 30+ ways to protect your WordPress sites with the SolidWP Security plugin.
Best Practices to Stop Brute Force Attacks on WordPress Sites
There are additional best practices you can implement to bolster your WordPress site’s defense against brute force attacks. By following these guidelines, you can significantly reduce the risk of unauthorized access and fortify your website’s security posture:
Use Strong and Unique Passwords
Encourage users to create complex passwords containing a mix of uppercase and lowercase letters, numbers, and symbols. Avoid common phrases or easily guessable information. Implementing a stringent password policy for all users can stop brute force attempts.
Implement Two-Factor Authentication (2FA)
Enabling 2FA adds an extra layer of security by requiring users to provide a secondary verification method, such as a smartphone app or SMS code, in addition to their password. This ensures that even if passwords are compromised, unauthorized access remains improbable.
Rename the Admin Account – (to Something Hard to Guess for Attackers)
Change the default ‘admin‘ username to something unique. Since ‘admin‘ is a common target, altering it makes it more challenging for attackers to guess the correct username during a brute-force attack.
Limit Login Attempts
Set a limited number of login attempts for both hosts and users. After a certain number of unsuccessful attempts, the system can automatically lock out the IP address, making it difficult for attackers to persistently try different login combinations.
Regularly Update WordPress, Themes, and Plugins
Outdated software can contain vulnerabilities that hackers exploit. Ensure your WordPress core, themes, and plugins are up-to-date to benefit from the latest security patches and enhancements.
Implement Web Application Firewall (WAF)
A WAF filters and monitors HTTP traffic between a web application and the Internet. It can prevent brute force attacks by blocking suspicious requests before they even reach your site.
Perform Regular Security Audits
Perform regular security audits on your WordPress site. Use security plugins to scan for vulnerabilities, malware, and suspicious activities. Timely detection can prevent potential brute force attacks.
Backup Your Website Regularly
Regularly back up your WordPress site, including databases and files. In case of a successful attack, having a recent backup ensures you can restore your site quickly and minimize downtime.
Monitor Server Logs
Regularly monitor server logs for unusual login activities or patterns. Unusual spikes in login attempts from specific IP addresses can indicate a brute force attack in progress. You can also track users’ activity on your WordPress site.
You create a multi-layered security shield around your WordPress site by implementing these best practices in conjunction with the steps outlined in the tutorial. Remember, proactive security measures are the key to safeguarding your website and user data against evolving cyber threats.
In conclusion, safeguarding your WordPress site against brute force attacks is paramount in today’s digital landscape, where cyber threats are rampant. With approximately 30,000 websites falling victim to hacking every day and a new cyberattack occurring every 39 seconds, it’s crucial to strengthen your website’s defenses.
To mitigate these risks, implementing robust security measures is essential. This tutorial outlined a comprehensive approach to protect your WordPress site using the SolidWP (formerly iTheme Security) plugin. By enabling local brute force protection, limiting login attempts per host and user, and banning hosts attempting to log in with common usernames like “admin,” you significantly reduce the vulnerability of your website.
Incorporating these steps not only enhances your website’s security but also safeguards your reputation and user data. Remember, staying proactive in your site’s security is key to ensuring a safe and trustworthy online presence.



